Digital Mapping: Transforming the Way We Navigate and Analyze Geographic Data
Introduction
Digital mapping has revolutionized the way we visualize, analyze, and interact with geographic data. Unlike traditional paper maps, digital maps are dynamic, interactive, and easily updated, enabling users to integrate multiple data layers for better decision-making.
A subset of this mapping, GIS (Geographic Information System) mapping, uses specialized software to analyze and interpret spatial data, making it a powerful tool for industries like public safety, urban planning, and environmental management. This includes the use for critical incident mapping solutions.
What Is Digital Mapping?
This refers to the process of creating and using maps in a digital format. It allows users to visualize spatial data, integrate real-time information, and perform advanced geographic analyses.
Key Components of Digital Mapping:
- Data Collection: Using tools like GPS, satellite imagery, and remote sensing to capture geographic data.
- Data Storage & Management: Storing spatial data in structured formats like GIS databases or cloud-based platforms.
- Data Visualization: Presenting geographic information using interactive maps, 3D models, and layers.
- Data Analysis: Applying algorithms and GIS tools to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within spatial data.
Applications of Digital Mapping
1. Public Safety & Emergency Response
- Enables real-time situational awareness for law enforcement, fire departments, and emergency medical services. These maps are considered critical incident mapping solutions and are extremely useful across schools.
- Helps first responders navigate efficiently using detailed GIS-enabled maps.
2. Schools & Educational campuses
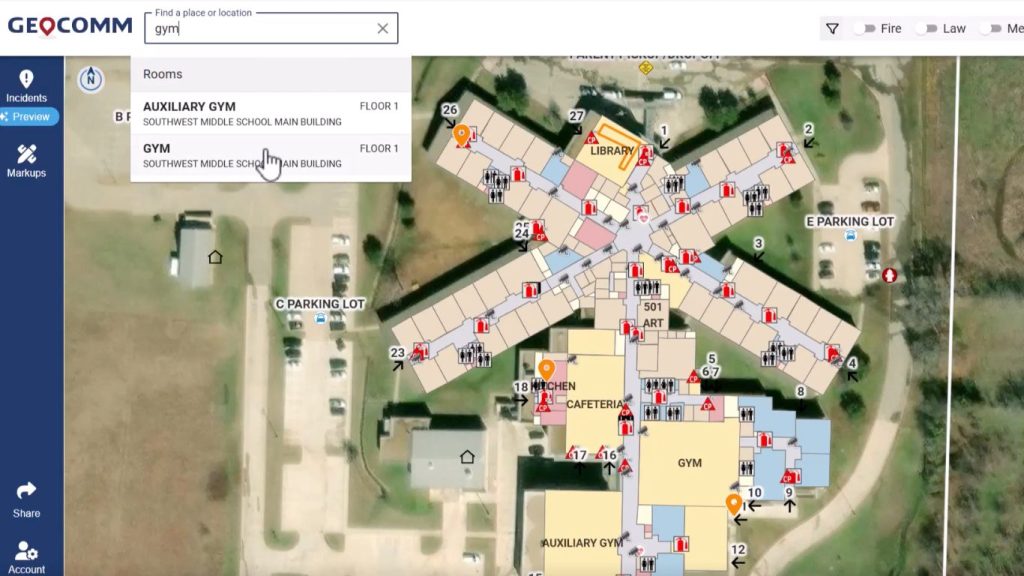
- Enhances emergency preparedness; providing first responders with accurate, interactive indoor and outdoor visualizations that pinpoint critical assets like exits, AEDs, and classrooms along with comprehensive searchable points of interest for more informed response during emergencies.
- Supports daily operations assisting school staff and facility management, space learning, and maintenance coordination by offering a centralized, updatable visual layout of the entire campus.
3. Urban Planning & Infrastructure Development
- Supports zoning, transportation planning, and land-use management with accurate spatial analysis.
- Assists in smart city initiatives, integrating real-time traffic data and resource management.
4. Environmental Conservation & Disaster Management
- Tracks deforestation, climate change, and natural disasters through satellite mapping.
- Assists in risk assessment and disaster response planning.
5. Business Intelligence & Market Analysis
- Helps businesses identify optimal locations for expansion by analyzing demographics and foot traffic.
- Supports logistics and supply chain optimization using route mapping technologies.
6. Navigation & Consumer Applications
- Powers GPS navigation apps like Google Maps, Apple Maps, and Waze.
- Enhances augmented reality (AR) experiences for location-based applications.
Challenges of Using PDFs
- Lack of Access Control: Once shared, PDF’s can be easily copied, forwarded, or accessed by unauthorized individuals, creating significant data exposure risks.
- No Audit Trail: PDF’s do not offer visibility into who accessed or modified the map, making it difficult to track and enforce data security protocols.
- Static and Outdated: PDFs cannot reflect real-time updates or be dynamically altered, which may leave outdated or sensitive information exposed without away to revoke or update it.
Benefits of Digital Mapping
- Accuracy & Precision: Provides highly detailed and real-time geographic information.
- Efficiency: Speeds up decision-making by visualizing complex data.
- Interactivity: Allows users to interact with maps dynamically (zooming, toggling layers, etc.).
- Integration Capabilities: Works with IoT, AI, and real-time data sources for enhanced analysis.
- Data Privacy & Security: Delivered through secure platforms that control who can view, edit, or share the data–minimizing unauthorized access.
Future Trends in Digital Mapping
- AI & Machine Learning Integration – Automating map analysis for predictive insights.
- 3D & Augmented Reality Mapping – Enhancing geospatial visualization in industries like real estate and gaming.
- Real-Time Data Streaming – Improving navigation, traffic monitoring, and crisis response.
- Crowdsourced Mapping – Leveraging user-generated content for more accurate maps.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How is digital mapping different from GIS mapping?
A1: Digital mapping is the broad process of creating and visualizing maps, while GIS mapping is a specific type of digital mapping that includes in-depth spatial analysis and data integration.
Q2: What industries benefit from digital mapping?
A2: Industries like public safety, urban planning, logistics, environmental management, and retail all benefit from digital mapping technologies.
Q3: What are some common digital mapping tools?
A3: Popular digital mapping platforms include Esri ArcGIS and GeoComm
Q4: Can digital mapping work offline?
A4: Yes, many mapping applications offer offline capabilities, allowing users to access pre-downloaded map data without an internet connection.
Q5: What role does AI play in digital mapping?
A5: AI helps analyze large datasets, predict trends, automate map updates, and improve navigation systems with real-time insights.
This style of mapping is more than just displaying geographic data—it’s a transformative technology that enhances decision-making across industries. From urban planning to real-time navigation, the power of interactive and data-driven maps continues to grow.
As GIS mapping and AI-driven geospatial technologies evolve, businesses and governments will increasingly rely on digital mapping for innovation and efficiency. A couple primary areas include critical incident mapping for safety across schools and large commercial properties.
Want to learn more about digital mapping based on geographic information system data?
How Minnesota First Responders Saved A Student’s Life using GeoComm School Safety
Speak to your Regional Manager for a free demo


